Curve widening Curve widening is required on both sides of the curve (FAO Watershed Management Field Manual, www.fao.org)
Curve widening is required on both sides of the curve (FAO Watershed Management Field Manual, www.fao.org)
Off-tracking on a curve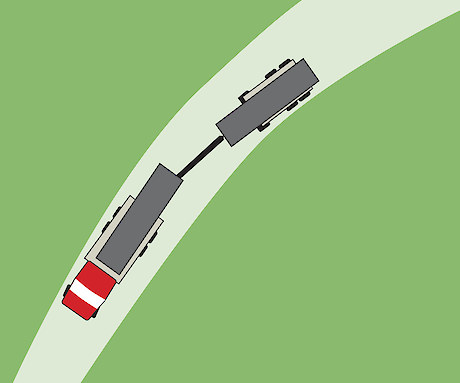 Trailer off-tracking on a curve. The magnitude of off-tracking depends on vehicle configuration, speed, corner radius and central angle (corner length)Additional widening at curves may be required to cater for trailer off-tracking. Curve widening is necessary to provide for the passage of loaded trailer axles outside of the truck wheel path and prevent them from tracking into the ditch. Curve widening is especially important when truck configurations with long drawbars and long trailers are intended to use the road.
Trailer off-tracking on a curve. The magnitude of off-tracking depends on vehicle configuration, speed, corner radius and central angle (corner length)Additional widening at curves may be required to cater for trailer off-tracking. Curve widening is necessary to provide for the passage of loaded trailer axles outside of the truck wheel path and prevent them from tracking into the ditch. Curve widening is especially important when truck configurations with long drawbars and long trailers are intended to use the road.
The amount of curve widening needed varies significantly depending on the truck configuration, corner radius and central angle (corner length). Since vehicles travel in both directions, half of the required curve widening should be added to the inside and half to the outside of the curve. A tapered road section should be provided to allow a transition both into and out of the corner.
Curve widening for truck/trailer combination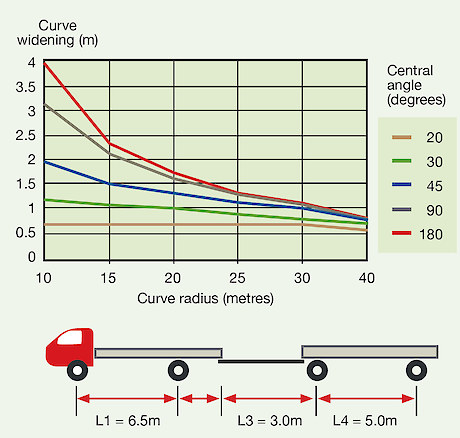 Curve widening for a typical truck/trailer configuration as a function of curve radius and central angle (www.fao.org)Curve widening for logging truck (pole trailer)
Curve widening for a typical truck/trailer configuration as a function of curve radius and central angle (www.fao.org)Curve widening for logging truck (pole trailer) Curve widening for a typical pole trailer configuration as a function of curve radius and central angle (www.fao.org)Some existing roads designed for 44 tonne and standard 4 axle trailer units may no longer be appropriate for 50t Max and HPMV configurations. Additional curve widening may be required to accommodate these.
Curve widening for a typical pole trailer configuration as a function of curve radius and central angle (www.fao.org)Some existing roads designed for 44 tonne and standard 4 axle trailer units may no longer be appropriate for 50t Max and HPMV configurations. Additional curve widening may be required to accommodate these.
The charts on this provide curve widening for two common vehicle configurations – a truck-trailer combination and a stinger-type logging truck. The charts are valid for the specified vehicle dimensions and configurations only. Equations enabling calculation of curve widening for other truck configurations can be found in Chapter 3 of the FAO Watershed Management Field Manual (FAO, 1990).